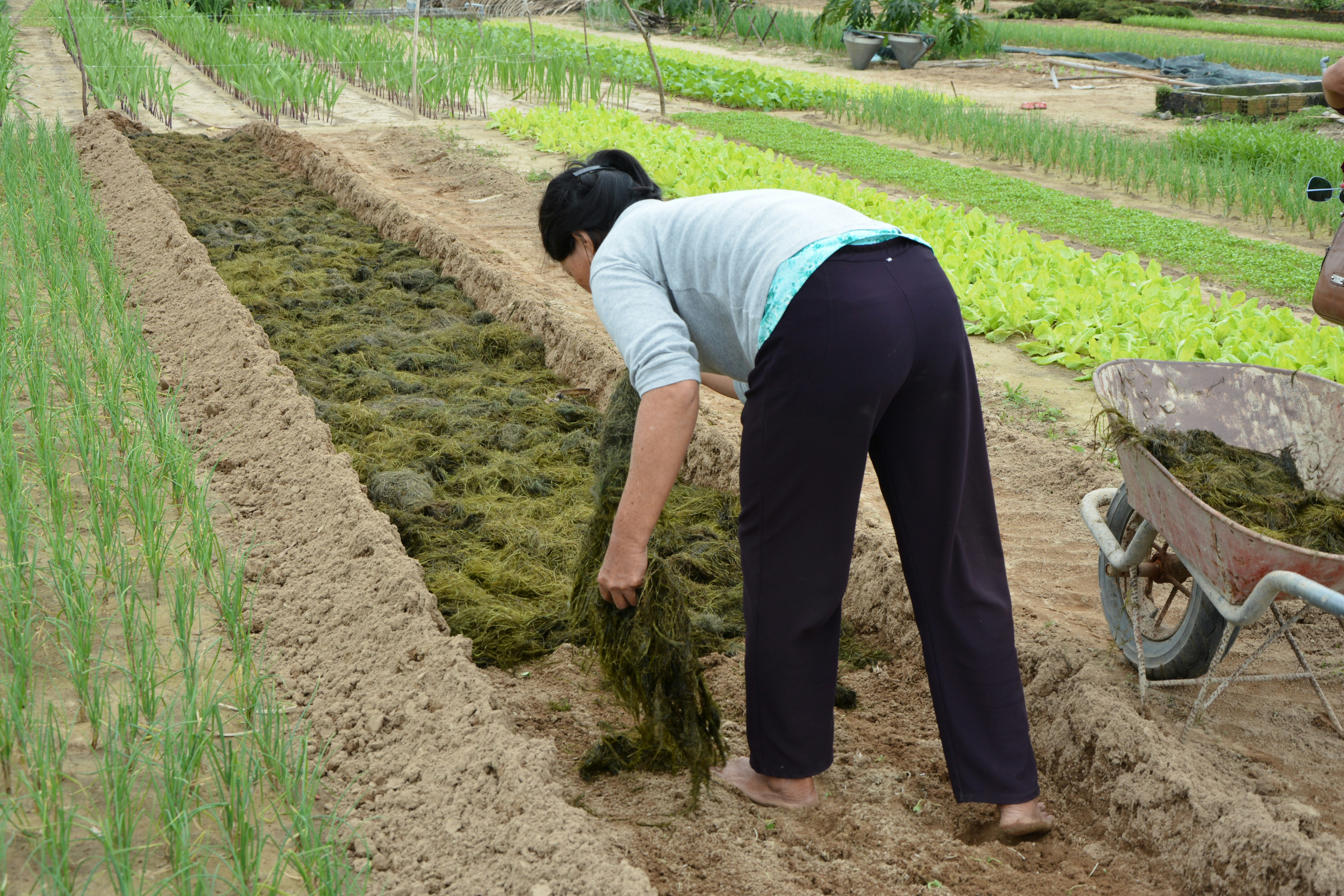
Bio-organic fertilizers represent a significant advancement in agricultural practices, differentiating themselves from conventional fertilizers through their natural composition. These fertilizers are derived from organic materials and are enriched with beneficial microorganisms, making them an excellent choice for promoting plant growth and enhancing soil health. Unlike traditional fertilizers, which often rely on synthetic chemicals, bio-organic fertilizers utilize the natural processes of decomposition and nutrient cycling. This sustainability aspect is crucial as it aligns with the growing demand for environmentally friendly farming methods.
The defining characteristic of bio-organic fertilizers lies in their formulation. They typically consist of composted plant materials, animal manure, and other organic substances that contribute essential nutrients to the soil. Furthermore, they often contain a diverse array of microorganisms, including bacteria and fungi, which play a vital role in breaking down organic matter and making nutrients available to plants. This microbial activity fosters a robust soil ecosystem, encouraging plant roots to absorb nutrients more efficiently and promoting vigorous growth.
One of the foremost benefits of employing bio-organic fertilizers is their positive impact on soil health. By increasing organic matter content, they improve soil structure and enhance its water retention capabilities, which is particularly important in arid regions. In addition to boosting soil fertility, these fertilizers mitigate chemical runoff, a significant concern with traditional fertilizers that can contribute to water pollution and adversely affect aquatic ecosystems. The use of bio-organic fertilizers not only fosters greater biodiversity in agricultural systems but also supports sustainable practices that are vital for long-term ecological balance.
In conclusion, bio-organic fertilizers offer a promising alternative to conventional fertilization methods, emphasizing natural composition, enhanced soil health, and environmental sustainability, all of which contribute to more resilient agricultural practices.
Bio-organic fertilizers are increasingly recognized for their numerous advantages over conventional fertilizers. One of the primary benefits lies in their capacity to improve soil structure and fertility. By incorporating organic matter, bio-organic fertilizers enhance the soil’s physical properties, making it more conducive to plant growth. This improved structure facilitates better aeration and root penetration, leading to healthier and more vigorous plants.
Another significant benefit is the enhanced water retention capabilities of soils treated with bio-organic fertilizers. These fertilizers help in building soil organic matter, which acts like a sponge that retains moisture. As a result, crops grown in such enriched soils can withstand periods of drought more effectively, reducing reliance on irrigation and improving water use efficiency. This characteristic is particularly advantageous as climate change increasingly leads to the unpredictability of weather patterns.
Moreover, bio-organic fertilizers foster beneficial microbial activity in the soil. A diverse microbial population is crucial for nutrient cycling and the decomposition of organic materials. This natural fermentation process enhances nutrient availability, which strengthens overall plant health. Enhanced nutrient absorption enables plants to develop better resistance against diseases and pests. Consequently, crops grow more robustly and yield more substantial harvests.
In addition to the immediate benefits for crops, the long-term advantages of adopting bio-organic practices extend to agricultural ecosystems. The use of bio-organic fertilizers contributes to a more sustainable farming practice, promoting biodiversity in the soil. Furthermore, these practices can lead to considerable cost savings for farmers; by reducing dependency on chemical inputs and synthetic fertilizers, they can lower production costs while maintaining high yield productivity.
Effectively applying bio-organic fertilizers is crucial for maximizing their benefits in both agricultural settings and home gardens. Various application methods are available, and selecting the appropriate technique can significantly impact the health of the crops and the environment. Timing and frequency of application are essential factors to consider. Depending on the crop type and growth stage, bio-organic fertilizers should generally be applied at the beginning of the planting season and during critical growth phases, such as flowering and fruiting.
Application rates can vary based on soil types and specific crop requirements. For most crops, a general guideline is to apply bio-organic fertilizers at a rate of 2 to 5 tons per hectare. However, it’s essential to conduct soil tests to tailor the application rate to the specific nutrient needs and existing soil fertility of your field or garden. This individualized approach ensures that the plants receive adequate nutrients without overwhelming the soil ecosystem.
There are several methods to apply bio-organic fertilizers effectively. Broadcasting involves spreading the fertilizer uniformly across the soil surface, which is suitable for crops that require broad nutrient availability. Top-dressing is another method where fertilizers are applied on the soil surface after the plants are already growing. This technique is particularly beneficial during critical growth periods, allowing for immediate nutrient uptake by the plants.
Incorporating bio-organic fertilizers into the soil is also a highly effective method. This can be done through plowing or mixing the fertilizer into the topsoil to enhance its contact with plant roots. Soil health plays a vital role in determining the successful application of bio-organic fertilizers. Regular testing of soil quality before and after application can help gauge the impact of fertilizers on soil biology and fertility, ultimately leading to improved agricultural practices. Understanding these application methods will empower farmers and gardeners to optimize the use of bio-organic fertilizers effectively.
The transition from conventional fertilization methods to bio-organic fertilizers presents several challenges for farmers and gardeners alike. One of the primary concerns during this initial period is the adjustment in nutrient availability. Unlike synthetic fertilizers, which often provide immediate and concentrated nutrition, bio-organic fertilizers release nutrients more gradually. Consequently, growers may encounter a lag in plant response, making it critical to monitor crops closely during this phase to avoid mismanagement of nutrient supply.
Furthermore, the variability in nutrient content found in bio-organic fertilizers necessitates thorough understanding and testing of these products before application. Unlike standardized synthetic fertilizers, the nutrient composition of organic variants can fluctuate based on the source material. Therefore, it is essential to evaluate the specific needs of your plants in conjunction with the properties of the bio-organic fertilizers being used. Conducting soil tests and analyzing local nutrient profiles can significantly mitigate potential deficiencies or excesses during the cultivation process.
Another consideration involves local soil conditions, which play a pivotal role in the effectiveness of bio-organic fertilizers. Different soil types possess unique properties that can influence nutrient absorption and microbial activity. Thus, it is advisable to familiarize oneself with local soil conditions before implementing bio-organic practices. Consultation with agronomists or specialized agricultural extension services can provide invaluable insights tailored to specific regional soil dynamics, ensuring that the transition is smooth and effective.
To overcome these challenges, ongoing education and research into bio-organic fertilizers are paramount. Engaging with local agricultural communities and exploring proven practices can aid in developing a successful strategy. Ultimately, a well-informed approach and professional guidance can greatly enhance the efficacy of bio-organic fertilizers, leading to sustainable and productive agricultural outcomes.